Accelerate to discover
Technologies
Type of the news
Brands



































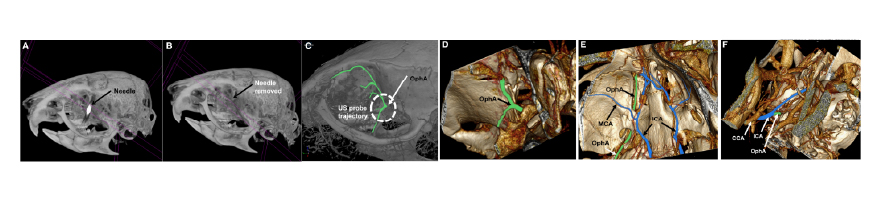
Non-invasive real-time pulsed Doppler assessment of blood flow in mouse ophthalmic artery
Imaging was performed under isoflurane anesthesia using the SkyScan 1276 instrument with an X-ray source voltage and current of 70 kV and 200 μA and a 1 mm Aluminum filter. A total of 1200 projection images were acquired at resolution of 13μm.
2026-02-06
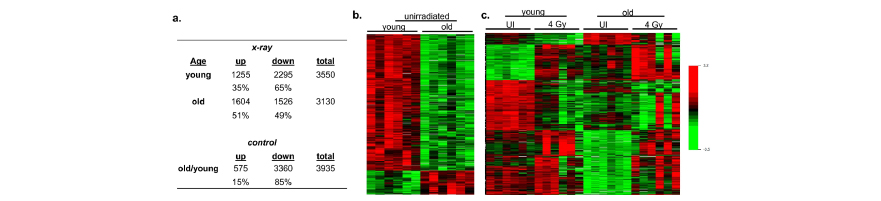
Impact of aging on gene expression response to x-ray irradiation using mouse blood
Mice were restrained in a pie holder without anesthesia and they were either sham-irradiated or exposed to 4Gy x-rays of total body irradiation from an X-RAD 320 Biological Irradiator.
2026-02-02
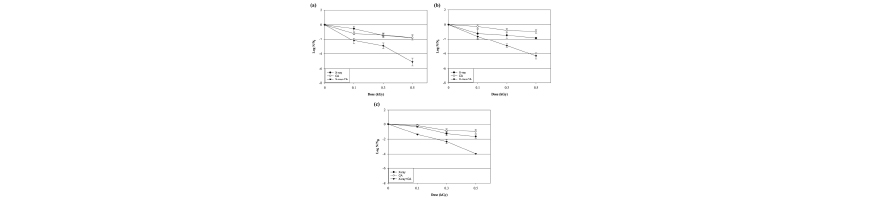
Combination of low-energy X-ray & citric acid to inactivate E.coli, S.Typhimurium, L.Monocitogenes
Combined treatment with 0.5 kGy X-ray and 0.1 % CA significantly decreased biofilm cell counts by 5.10, 4.31, and 3.96 log CFU/coupon for E. coli O157:H7, S. Typhimurium, and L. Monocytogenes, respectively.
2025-12-03
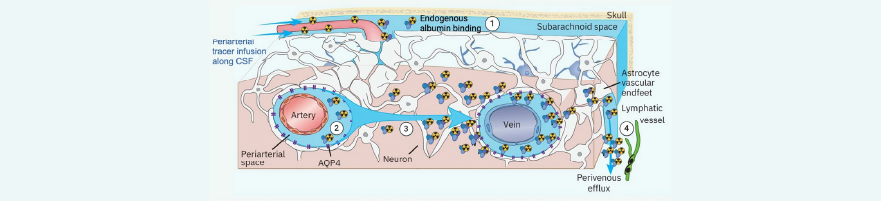
Development of new albumin‑binding radiotracers for PET imaging of CSF
In this study by Peltoniemi et al., PET/CT imaging using the X-CUBE (CT) and ß-CUBE (PET) was used to non-invasively visualize cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow and glymphatic system dynamics in rats.
2025-11-28
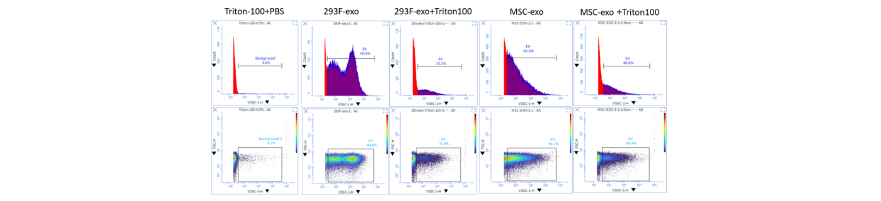
Measure EV Purity Results by Calculating the Membrane Ratio with the Exoplorer
Working with Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)? Imagine being able to effortlessly measure EV quality. This is possible with the Exoplorer™ Nano-flow Cytometer — a highly effective tool for nanoparticle-level analysis.
2025-10-20
Optimizing Substrate Dosing for ReliableBioluminescence Imaging (BLI)
Bioluminescence imaging relies on precise D-luciferin administration, as dosing variability impacts signal intensity and data consistency. Standardizing substrate delivery is essential for reproducible and high-quality in vivo imaging results.
2025-09-18
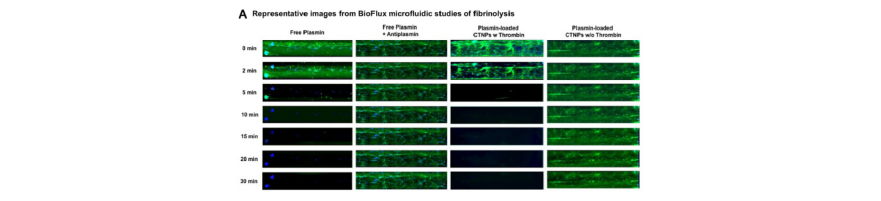
Direct delivery of plasmin using clot-anchoring thrombin-responsive nanoparticles
The targeted fibrinolytic efficacy of the plasmin-loaded CTNPs was then evaluated under flow using the Bioflux microfluidic device.
2026-01-28
The Path to Clinical Relevance: Moving from Spatial Transcriptomics to Protein Profiling
Spatial biology is a rapidly evolving discipline that advances human health by leveraging imaging technologies. It encompasses research activities ranging from whole-transcriptome profiling to clinically impactful single-protein biomarker tests.
2025-12-02
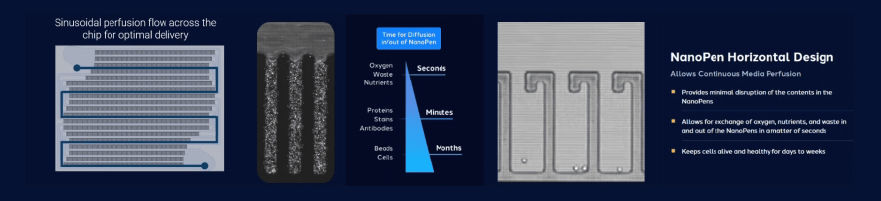
Perfusion: The Beating Heart of Single-Cell Biology and Cancer Immunotherapy
Single-cell biology has transformed our ability to uncover cellular diversity and dynamic behavior within complex tissues that are otherwise masked in population-level analyses.
2025-11-24
Automated and efficient isolation of single cells into low volumes for scWGA
Single-cell whole-genome amplification (scWGA) is a powerful technique to massively amplify and analyse the genomes of individual cells.
2025-10-17
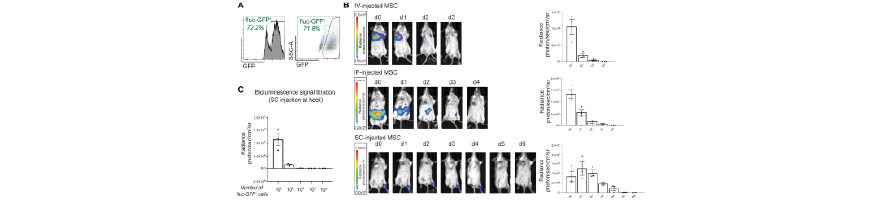
Subcutaneous delivery of MSC induces immunoregulatory effects in the lymph node
Mice were imaged under anaesthesia (2.5% isoflurane in oxygen), daily until the bioluminescence signal disappeared. Imaging was performed in an Ami-HTX Small Animal Imager and analysed with Aura Imaging Software, from Spectral Instruments Imaging.
2025-09-12
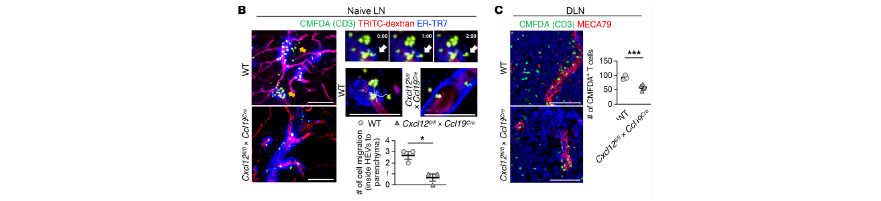
CXCL12+ fibroblastic reticular cells in lymph nodes facilitate immune tolerance
The popliteal LNs were exposed surgically and confocal intravital imaging was performed (IVM-CMS3). Twenty-five Z-stack images were obtained with a 3 μm axial interval. Time-lapse images were obtained at a 1-minute time interval for 20 minutes.
2026-01-26
Can you solve mouse CT imaging with 50um spatial resolution ?
MOLECUBES, a Bruker Company offers small footprint microCT for mice and rats, which meets most of your needs for in-vivo analysis and doesn't sacrifice the budget.
2025-10-22
Refining Biomedical Research Beyond Animal Models
What the Pivot to Human-Based Technologies Means for Science and How 3D Cellular Constructs like Organoids Are Part of the Solution.
2025-10-13