Molecular technologies
Targeted DNA/protein size collection & Imaging
DNA or cDNA sizing and protein fractionation
The technology is built on the idea that science is more robust and reliable when it is based on high-precision, automated, reproducible technology instead of manually intensive steps that introduce variability and error.
Molecular biology workflows can be significantly improved with accurate, automated solutions. Our technology not only reduces hands-on time and boost throughput, but they also improve data quality and downstream results.
The Sage Science portfolio includes products to perform DNA or cDNA sizing and protein fractionation.
Targeted DNA Size Selection: Pippin
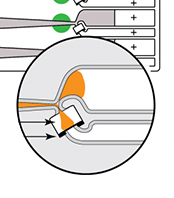
Pippin’s disposable gel cassettes are precast with agarose. DNA sizing is determined by the detection of markers in a dedicated lane or internally in the sample lane and using those to select and collect the desired fragments based on user-input values.
Each sample lane is physically separate to eliminate the possibility of sample cross-contamination and features a branched configuration with three electrodes. DNA is separated along a gel column until the programmed fragment range reaches the branch point. The instrument then switches the active electrode to divert DNA into a membrane-bound buffer chamber. When the size range has been collected, the active electrode is switched back to the separation channel. The desired sample can be removed with a standard pipette.
DNA sizing is available with the Pippin Prep (for fragments from 90 bp to 1.5 Kb) and with the BluePippin (a pulsed-field version for fragments from 50 bp to 50 Kb).
Whole-Sample Fractionation for DNA or Protein: SageELF
The fully automated SageELF (for Electrophoretic Lateral Fractionator) can be used to select DNA or proteins. It features a cassette system designed to fractionate a whole protein or DNA sample simultaneously into 12 contiguous size fractions.
For proteomics users, SageELF delivers 12 size fractions in SDS buffer ready for analysis or identification on a mass spectrometer.
For scientists working with DNA, the generation of 12 contiguous fractions maximizes the utility of precious samples and can be used to build multiple libraries of different insert sizes for both short-read sequencers and long-range technologies that can assess structural information.