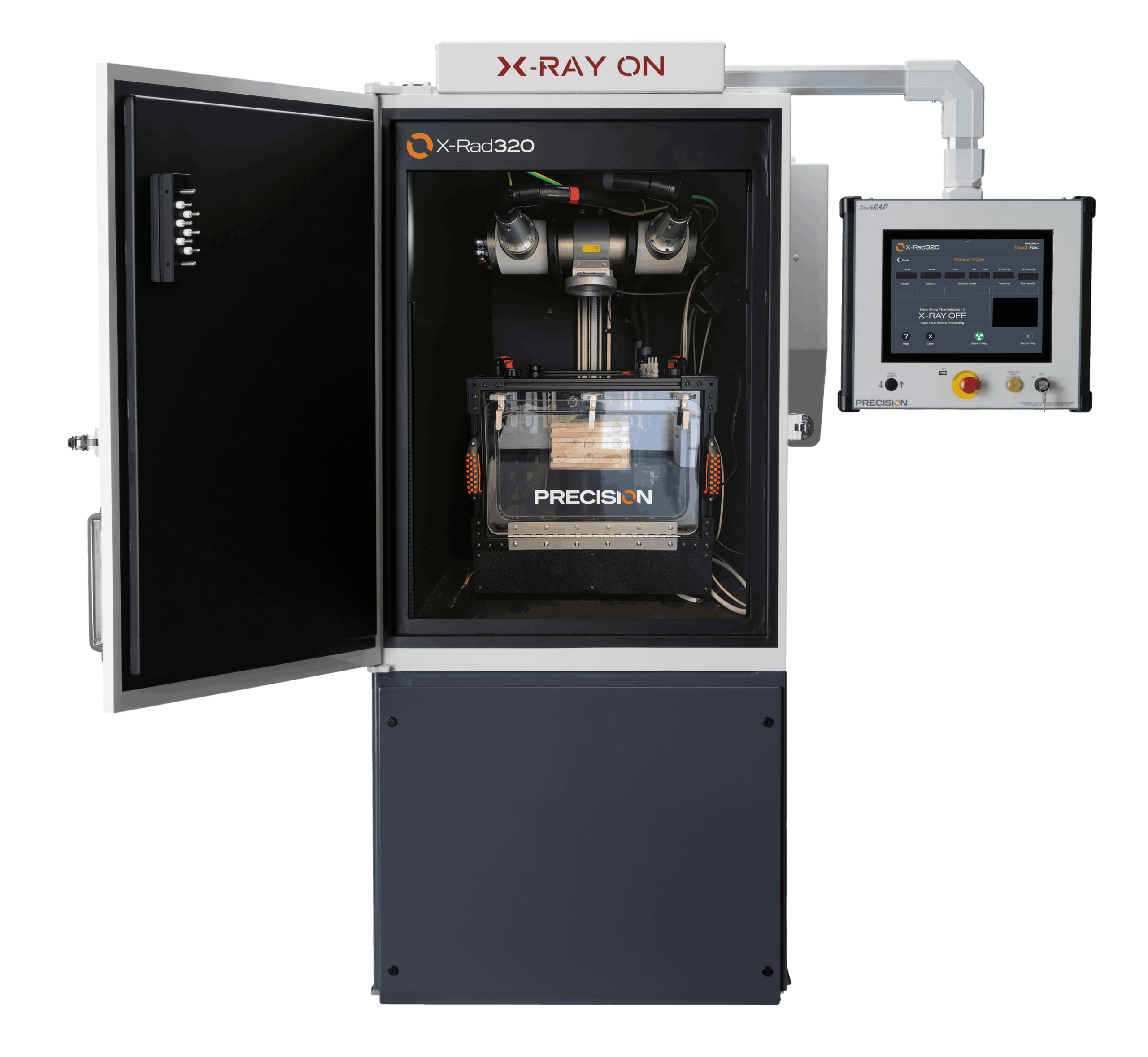
Precision X-ray is the leading provider of safe, high output X-Ray irradiators used in modern translational research.
Accelerate to discover
Related topics
X-RAD 320 for irradiation therapy during quantifying study for in vivo collagen reorganization
X-RAD 320 for irradiation therapy during quantifying study for in vivo collagen reorganization
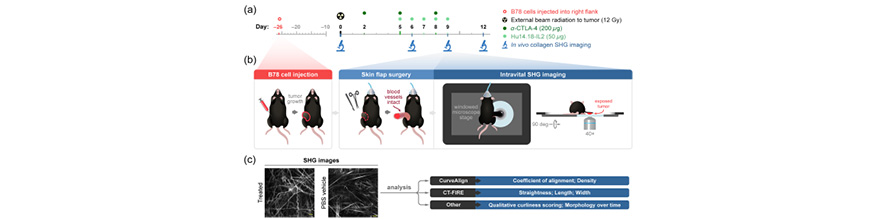
Increased collagen linearization and deposition during tumorigenesis can impede immune cell infiltration and lead to tumor metastasis. Although melanoma is well studied in immunotherapy research, studies that quantify collagen changes during melanoma progression and treatment are lacking.
Second-harmonic generation imaging of collagen was performed in mouse melanoma tumors in vivo over a treatment time course. Animals were treated with a curative radiation and immunotherapy combination. Collagen morphology was quantified over time at an image and single-fiber level using CurveAlign and CT-FIRE software.
Results
In immunotherapy-treated mice, collagen was reorganized toward a healthy phenotype, including shorter, wider, curlier collagen fibers, with modestly higher collagen density. Temporally, collagen fiber straightness and length changed late in treatment (days 9 and 12), while width and density changed early (day 6) compared with control mice. Single-fiber collagen features calculated in CT-FIRE were the most sensitive to the changes among treatment groups compared with bulk collagen features.
Conclusions
Quantitative second-harmonic generation imaging can provide insight into collagen dynamics in vivo during immunotherapy, with key implications in improving immunotherapy response in melanoma and other cancers.
Related technologies: X-ray irradiation




